Learn in Public
Mon Jul 01 2024
•Learning to write while writing to learn.
Exploring the Power of JavaScript
JavaScript is the backbone of modern web development. From simple scripts to complex applications, it powers much of what we see and interact with on the web today. In this article, we'll explore some of the most powerful features of JavaScript and how they can be leveraged to build robust applications.
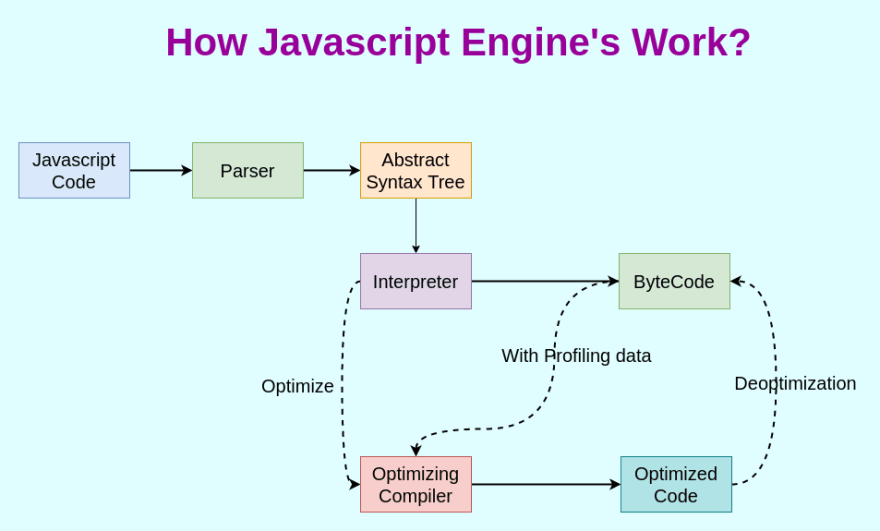
Understanding Variables and Data Types
In JavaScript, variables are used to store data. You can declare a variable using var, let, or const. The difference lies in their scope and mutability.
let message = "Hello, World!";
const pi = 3.14159;
var count = 42;
In the example above:
messageis a variable that can be reassigned.piis a constant that cannot be changed.countis a variable declared using the oldvarkeyword.
Working with Functions
Functions are one of the core building blocks in JavaScript. They allow you to encapsulate code and reuse it throughout your application.
function greet(name) {
return `Hello, ${name}!`;
}
const greeting = greet("Alice");
console.log(greeting); // Outputs: Hello, Alice!
In this code snippet, the greet function takes a name parameter and returns a greeting message. This function can be reused with different names.
Comparing == and ===
One of the common pitfalls in JavaScript is the difference between == and ===.
==checks for equality after type conversion.===checks for equality without type conversion, meaning both value and type must be the same.
console.log(5 == "5"); // true, because "5" is converted to 5 before comparison
console.log(5 === "5"); // false, because 5 and "5" are of different types
To avoid unexpected behavior, it's generally recommended to use === for comparisons.
JavaScript Array Methods
JavaScript provides a rich set of methods to manipulate arrays. Here are some of the most commonly used ones:
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
push() |
Adds one or more elements to the end of an array | arr.push(4) adds 4 to the end of arr |
pop() |
Removes the last element from an array | arr.pop() removes the last element |
map() |
Creates a new array with the results of calling a function on every element | arr.map(x => x * 2) doubles each element |
filter() |
Creates a new array with all elements that pass the test implemented by the provided function | arr.filter(x => x > 10) returns elements greater than 10 |
reduce() |
Executes a reducer function on each element of the array, resulting in a single output value | arr.reduce((a, b) => a + b) sums the elements |
Asynchronous Programming
Asynchronous programming is a key feature of JavaScript, allowing you to perform tasks like fetching data from an API without blocking the main thread.
async function fetchData() {
const response = await fetch('https://api.example.com/data');
const data = await response.json();
console.log(data);
}
fetchData();
In this example, the fetchData function asynchronously fetches data from an API and logs it to the console.
Conclusion
JavaScript is a versatile and powerful language, capable of handling a wide range of tasks, from basic scripts to complex applications. By understanding and leveraging its features, you can create more efficient, maintainable, and scalable code.